What is a Computer?
Two paths that began independently but converged in the 20th century.
- Engineering a mechanical calculator
- Ancient astronomical calculators, using gears
- Adding machines from the time of Pascal and Leibniz
- Babbage's difference engine
- First programmer Ada Lovelace
- Modern electric digital computers
- Looking for an epistemic foundation for math
- Axiomatic systems
- David Hilbert's Entscheidungsproblem ("the decision problem")
- Computability
- Turing machine
- Others - Lambda calculus (Church), Recursive functions(Godel), Combinatory logic (Schonfinkel and Haskell Curry), Production systems (Post), Markov algorithms (Markov)
- Axiomatic systems
Paths converge around the time of von Neumann architecture
Logical Properties and Formal Proofs
Here's an xor circuit:
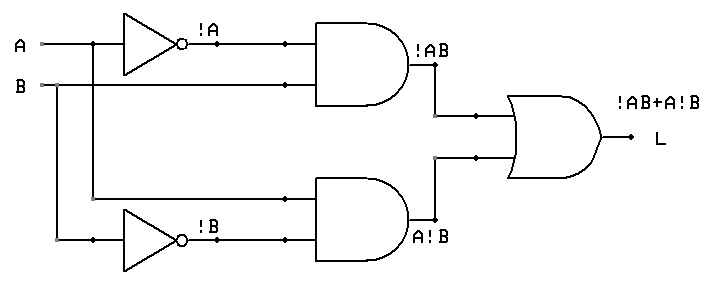
Last time we saw that there were 9 logical properties that are of interest. Here we should reflect on why we care about such properties, which can be demonstrated by a formal proof, which can't, and why.
| . | Shown by considering all possibilities or by formal proof | Shown by example or instance |
|---|---|---|
| Argument | Valid if for every possibility, if the premises are true, the conclusion is also true. Derive the conclusion from the premises. | Invalid if in at least one case the premises are true and the conclusion is false |
| Set of sentences | Jointly impossible if in every possibility at least one sentence is false. Derive a contradiction from the sentences | Jointly possible if in at least one case all are true |
| Pair of sentences | Equivalent if in every possibility they have the same truth value. Derive first sentence from the second and vice versa | Not equivalent if they differ in truth value in at least one cases |
| Sentence | Necessarily true if true in every possibility (derive with no premises) and necessarily false if false (derive a contradiction from the sentence) in every possibility | Contingent if true in at least one case and false in at least one case (two examples) |
Today, more practice working through the worksheet, using the formal proof/example method.